Those of us lucky enough to be sitting by a window can predict the weather just by looking outside, but for the less privileged, weather forecasting and analysis is getting better and better. Tomorrow.io just released the results from its first two radar satellites, which, thanks to machine learning, turn out to be competitive with larger, more old-school forecasting tech on Earth and in orbit.
The company has been planning this mission since it was called ClimaCell, back in 2021, and the results being released today (and formally presented at a meteorology conference soon) show that their high-tech approach works.
Weather prediction is complex for a lot of reasons, but the interplay between high-powered but legacy hardware (like radar networks and older satellites) and modern software is a big one. That infrastructure is powerful and valuable, but to improve their output requires a lot of work on the computation side — and at some point you start getting diminishing returns.
This isn’t just “is it going to rain this afternoon” but more complex and important predictions like which direction a tropical storm will move, or exactly how much rain fell on a given region over a storm or drought. Such insights are increasingly important as the climate changes.
Courtesy of AI: Weather forecasts for the hour, the week and the century
Space is, of course, the obvious place to invest, but weather infrastructure is prohibitively big and heavy. NASA’s Global Precipitation Measurement satellite, the gold standard for this field launched in 2014, uses both Ka (26-40 GHz) and Ku (12-18 GHz) band radar, and weighs some 3,850 kilograms.
Tomorrow.io’s plan is to create a new space-based radar infrastructure with a modern twist. Its satellites are small (only 85 kilograms) and use the Ka-band exclusively. The two satellites, Tomorrow R1 and R2, launched in April and June of last year, are just now, after a long period of shake-out and testing, beginning to show their quality.
In a series of experiments that the company is planning to publish in a journal later this year, Tomorrow claims that with only one radar band and a fraction of the mass, their satellites can produce results on par with NASA’s GPM and ground-based systems. Across a variety of tasks, the R1 and R2 satellites were able to make similarly accurate or even better and more precise predictions and observations as GPM, and their results also tallied closely with the ground radar data.
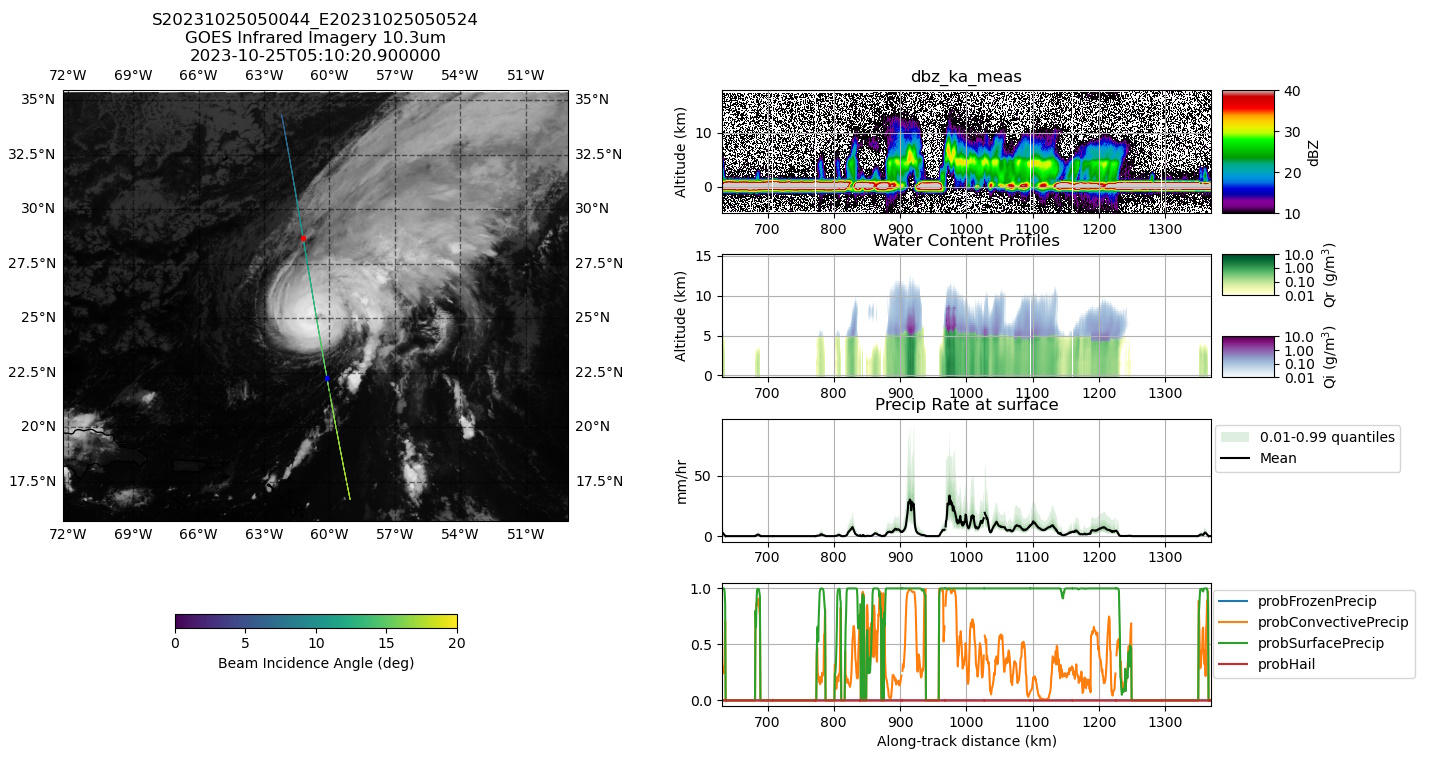
They accomplish this though the use of a machine learning model that, as Chief Weather Officer Arun Chawla described it, acts as two instruments in one. It was trained on data from both of the GPM’s radars, but by learning the relationship between the observation and the difference between the two radar signals, it can make a similar prediction using just one band. As their blog post puts it:
The algorithm is trained with these dual-frequency-derived precipitation profiles but only uses the Ka-band observations as input. Nevertheless, the complex relationship between the reflectivity profile shape and precipitation is “learned” by the algorithm, and the full precipitation profile is retrieved even in cases where the Ka-band reflectivity is completely attenuated by heavy precipitation.
It’s a big success for Tomorrow.io if these results pan out and generalize to other weather patterns. But the idea isn’t to replace the U.S. infrastructure — GPM and the ground radar network are here for the long haul and are invaluable assets. The real problem is that they can’t be duplicated easily to cover the rest of the world.
The company’s hope is to have a network of satellites that can provide this level of detailed prediction and analysis globally. Their eight planned production satellites will be bigger — around 300 kg — and more capable.
“We are working on providing real-time precipitation data anywhere in the world, which we believe is a game changer in the field of weather forecasting,” Chawla said. “In that respect we are working on accuracy, global availability and latency (measured as the time between the signal being captured by the satellite and the data being available for ingesting into products).”
They’re also making the inevitable data play, with a more detailed set of orbital radar imagery to train their own and other systems on. For that to work, they’ll need lots more data, though — and they plan to pick up the pace collecting it with more satellite launches this year.