Varda Space Industries has closed a massive tranche of funding just weeks after its first drug manufacturing capsule returned from orbit.
The company’s $90 million Series B round marks an inflection point for the company, which is now gearing up to scale from the initial demonstration mission to a regular set of missions carrying customer payloads, Varda founder Delian Asparouhov told TechCrunch.
El Segundo-based Varda was founded in 2021 by Asparouhov, who is also a partner at Founders Fund, and Will Bruey, a spacecraft engineer who cut his teeth at SpaceX. The pair had an audacious goal to commercialize what until very recently was promising but ultimately small-scale research into the effects of microgravity on pharmaceutical crystals.
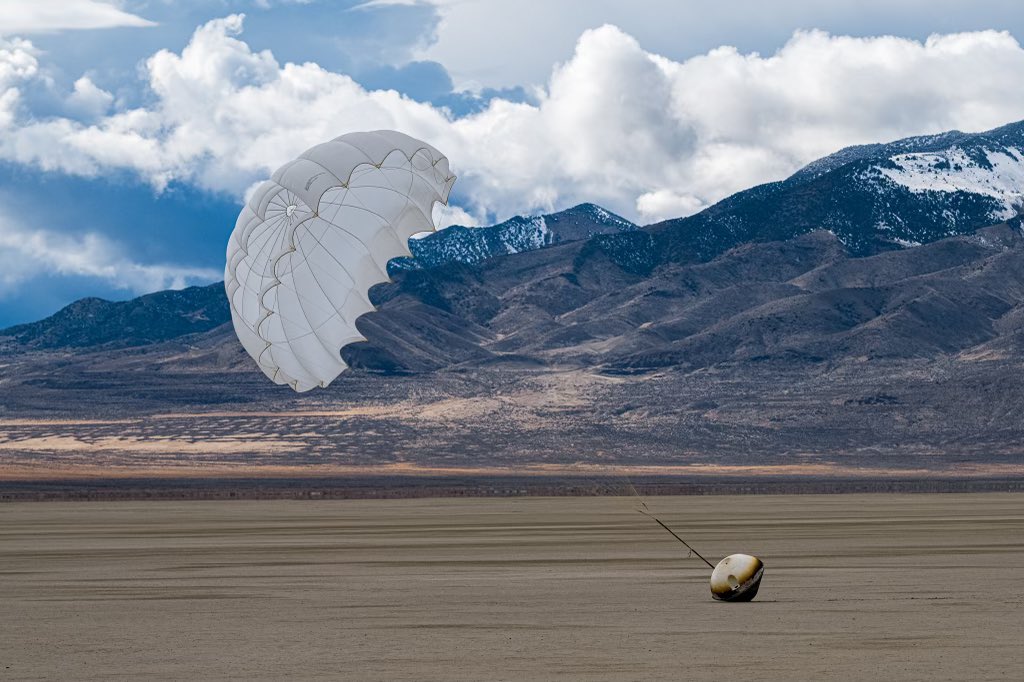
Indeed, Varda’s first mission, which returned to Earth in February after 10 months in orbit, does not mark the first time a drug has been crystallized in microgravity. Astronauts have been conducting protein crystallization experiments in space for decades on the International Space Station and before that, the Space Shuttle.
But the business case for expanding this research has never materialized — until now. This is for a few different reasons, Asparouhov explained: because of the crew, there are significant limitations to the types of solvents or other materials you can bring onboard the ISS; there are constraints related to intellectual property for work that happens on the station; and pharmaceutical lab equipment designed for use in-space was generally lacking in sophistication compared to the terrestrial versions.
But much has changed, especially in the space industry. Part of the reason Varda is possible today is due to the availability of regular, low-cost rideshare launches from SpaceX and Rocket Lab’s innovations in satellite bus manufacturing. Even beyond these external partnerships, the startup has made significant headway in its own right, as the success of the first mission showed: Their reentry capsule appears to have performed flawlessly and the experiment to reformulate the HIV medicine ritonavir was executed without a hitch, it says.
Varda has also started publishing the results of its internal R&D efforts, including a scientific paper on its hyper-gravity (as opposed to microgravity) crystallization platform, which the startup developed as a sort of screening method prior to sending drugs to space. It’s an entirely new field of research that takes advantage of the ability to truly unlock gravity as a variable in scientific experiments.

“Over time, we will be able to generate data sets between both hyper-gravity and microgravity and start to show correlations,” he said. “As Varda flies more and more, we are confident that we will start to be able to develop systems of thinking where, for patterns of particular types of chemical systems, hyper-gravity will be used as a way to determine the correlation between, ultimately, microgravity and the drug performance.”
There’s still lots of work ahead. While engineers will study this first spacecraft, called Winnebago, to understand the wear and tear on the vehicle, the company as a whole will focus more on cadence before reusability, he said.
“If you just amortize the total cost to operate the business, we have so much more to gain by initially increasing cadence of flights before we really started to go for reusability. In some ways, it’s like we need to get to a once-a-month cadence before reusability is actually the biggest lever for us.”
Varda does aim to significantly drive down mission costs by refurbishing and reusing the Winnebago capsules, as SpaceX does with its Dragon capsule, but Asparouhov said that won’t happen until later in the decade, around 2027. (In a recent podcast appearance, he specified that the all-in initial mission cost around $12 million, which will drop to $5-6 million by mission 4 and $2.5 million or less by mission 10.) Larger capsules are also in the longer-term pipeline, though also not until the 2027 time frame.
Asparouhov also confirmed that pharmaceuticals will be Varda’s sole focus for the next 10-20 (or more) years, based on the company’s conviction that pharmaceutical products will generate more economic value compared to other materials. A lot of that comes down to the fact that there are a significant set of drugs that require only a “seed” of the material that can only be made in microgravity, and the rest of the drug formulation can be completed here on Earth. That means the product is high revenue but low mass.
The company is also aiming to improve the processing capabilities of the on-board pharmaceutical reactor. The first mission carried just one drug protein, but in the future the company hopes to process multiple drug products that could be run through different processing regimes. In the future, other missions could carry larger reactors for drugs that do need more than the “seed” crystal, and those mission profiles would be closer to something like mass manufacturing.
Varda has “a handful” of signed contracts with publicly traded biotech companies, and the next three missions already manifested with Rocket Lab, which provided the spacecraft bus for mission 1. The startup’s next manufacturing mission will launch later this year, and the team plans to land that spacecraft in Australia.
The new financing was led by Caffeinated Capital, with participation from Lux Capital, General Catalyst, Founders Fund and Khosla Ventures. Varda has now raised $145 million to date.